Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definitions and Key Concepts
- Wound Evisceration vs Dehiscence: Comparison Table
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Management and Prevention
- Medical Training with Simulation Models
- Company Spotlight: Medtacedu
- FAQs
- References
Introduction
When it comes to postoperative care, understanding wound evisceration vs dehiscence is crucial for healthcare professionals. Both conditions represent serious complications of surgical incisions, but they differ in severity and clinical management. Proper education and training, particularly through realistic medical models, can help clinicians recognize and manage these conditions effectively.
Definitions and Key Concepts
What is Wound Dehiscence?
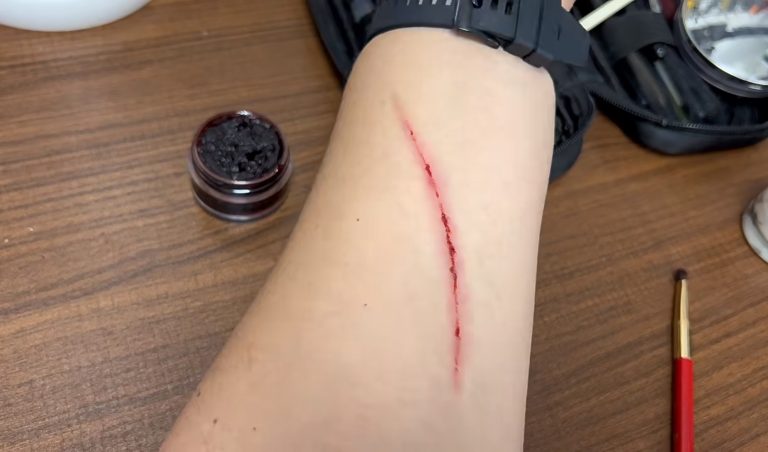
Wound dehiscence refers to the partial or complete reopening of a surgical incision after closure. It typically occurs within the first week after surgery, often due to infection, poor wound healing, or excessive strain on sutures. Recognizing early signs, such as serosanguinous discharge or increased pain, is vital for prevention.
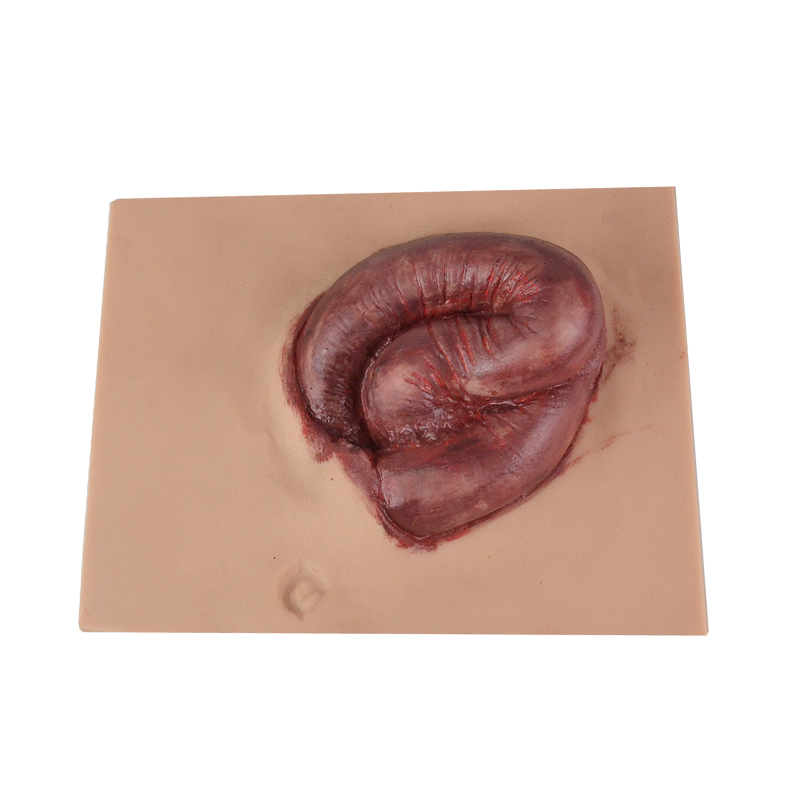
What is Wound Evisceration?
Wound evisceration is a more severe form of wound dehiscence where abdominal organs, particularly the intestines, protrude through the open incision. It is a surgical emergency requiring immediate intervention to prevent infection, tissue desiccation, and necrosis.
Key Point: While dehiscence represents separation of wound layers, evisceration involves protrusion of internal organs — making it a life-threatening event.
Wound Evisceration vs Dehiscence: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Wound Dehiscence | Wound Evisceration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partial or complete separation of wound layers. | Protrusion of abdominal organs through a dehisced wound. |
| Severity | Moderate complication. | Severe surgical emergency. |
| Symptoms | Wound gaping, drainage, pain. | Visible organ protrusion, shock, infection risk. |
| Management | Antibiotics, wound care, re-suturing if needed. | Cover organs with moist sterile dressing, emergency surgery. |
| Prevention | Proper suturing, nutrition, patient education. | Prevent dehiscence; treat early before progression. |
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes
- Infection at surgical site
- Obesity or poor nutritional status
- Diabetes mellitus
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure (e.g., coughing, vomiting)
- Inadequate suturing techniques
Risk Factors
Patients with chronic diseases, smokers, or those on corticosteroids are at higher risk. Early recognition and careful postoperative management are crucial for reducing cases of wound evisceration vs dehiscence.
Management and Prevention
Initial Steps in Dehiscence
- Stop activities increasing strain on incision.
- Apply sterile dressings.
- Notify the surgical team for assessment.
Emergency Response in Evisceration
- Do not attempt to push organs back inside.
- Cover exposed organs with sterile saline-soaked gauze.
- Call for immediate surgical intervention.
Preventive Measures
Prevention of both wound evisceration vs dehiscence involves proper wound closure techniques, infection control, patient education, and realistic medical training for healthcare staff.
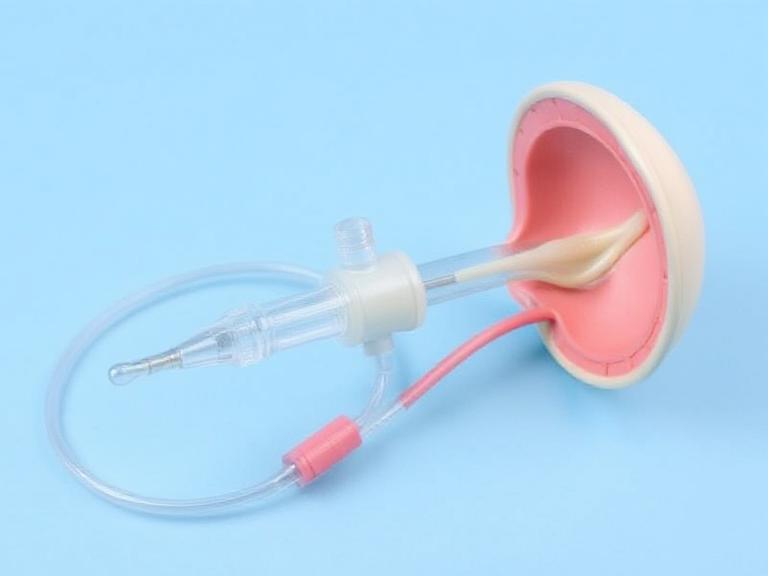
Medical Training with Simulation Models

To train healthcare professionals effectively, the use of medical simulation is invaluable. Simulation models allow repeated practice in safe, controlled environments, improving decision-making and response speed.
- Realistic representation of human tissue.
- Hands-on learning for wound assessment.
- Safe environment for emergency scenario training.
Company Spotlight: Medtacedu

Medtacedu is a trusted name in medical education tools, producing high-quality silicone and plastic models for tactical training, medical education, and science instruction. Their products serve as crucial tools in understanding complex medical events such as wound evisceration vs dehiscence.
What Our Products Can Do
- Tactical Training: Wound dressing models, trauma manikins, and comprehensive training kits for real-world medical readiness.
- Medical Demonstration and Training: Silicone-based disease and wound models for surgical simulation and education.
- Science Education: Customizable veterinary and anatomical models for classroom or research settings.
- Injection Models: Specialized ID/SC/IM/IV injection training models, including facial models for Botox and dermal injections.
Why Choose Medtacedu?
- Extensive Product Range supporting resellers and institutions.
- Over 16 years of production expertise in silicone medical model manufacturing.
- Customizable solutions for universities, hospitals, and research centers.
Our Product Categories
- Medical Models
- Tactical Training Models
- Injection Models
- Beauty Injection Models
- Medical Simulators
Medtacedu’s medical models enhance understanding of surgical complications such as wound evisceration vs dehiscence, empowering healthcare providers to save lives through better training.
FAQs: Wound Evisceration vs Dehiscence
1. How is wound evisceration different from dehiscence?
Dehiscence involves wound separation, while evisceration is when internal organs protrude through that wound. The latter is a surgical emergency.
2. Can wound evisceration occur without prior dehiscence?
No. Evisceration always occurs as a progression of severe dehiscence.
3. How can simulation models improve training outcomes?
Simulation models provide realistic hands-on practice, reducing errors in actual patient care.
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Postoperative Wound Management.
- Medscape: Surgical Complications
- Medtacedu Official Site – Medical Training Models