Table of Contents
- 1. What is Abdominal Evisceration?
- 2. Causes of Abdominal Evisceration
- 3. Signs and Symptoms
- 4. Emergency Treatment
- 5. Surgical Management
- 6. Prevention and Safety Measures
- 7. Importance of Medical Simulation Training
- 8. Company Spotlight: Medtacedu
- 9. Summary Table
- 10. FAQs
- 11. References
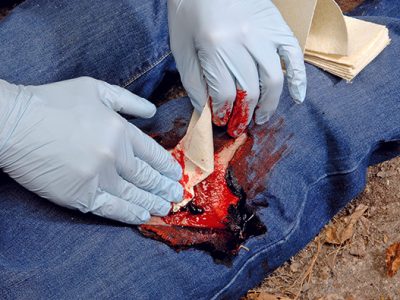
1. What is Abdominal Evisceration?
Abdominal evisceration refers to a severe medical emergency where internal abdominal organs, such as the intestines, protrude through a wound in the abdominal wall. This can result from trauma, surgical complications, or spontaneous wound dehiscence. Because abdominal evisceration exposes internal organs to the external environment, it requires immediate medical intervention to prevent infection, tissue necrosis, and other life-threatening complications.

In surgical and emergency settings, healthcare professionals must act swiftly to stabilize the patient, control contamination, and prepare for surgical repair. Understanding the anatomy, causes, and procedures involved in abdominal evisceration is vital for surgeons, nurses, and first responders.
2. Causes of Abdominal Evisceration
The causes of abdominal evisceration can be broadly categorized into traumatic, postoperative, and spontaneous cases. Below are the main causes:
2.1 Traumatic Causes
- Penetrating injuries (e.g., stab or gunshot wounds)
- Severe blunt force trauma causing rupture of the abdominal wall
- Industrial or vehicular accidents
2.2 Postoperative Causes
- Wound dehiscence after abdominal surgery
- Poor wound healing due to infection or tension on the sutures
- Obesity or chronic coughing increasing abdominal pressure
2.3 Spontaneous Evisceration
- Weakness in surgical scars
- Underlying tissue necrosis or poor blood supply
- Severe infection compromising the wound site
3. Signs and Symptoms
The presentation of abdominal evisceration is often dramatic and easily recognizable. Common symptoms include:
- Visible intestines or organs outside the abdominal cavity
- Severe abdominal pain and tenderness
- Bleeding and shock
- Distress and anxiety due to visible trauma
- Possible contamination with foreign materials or dirt
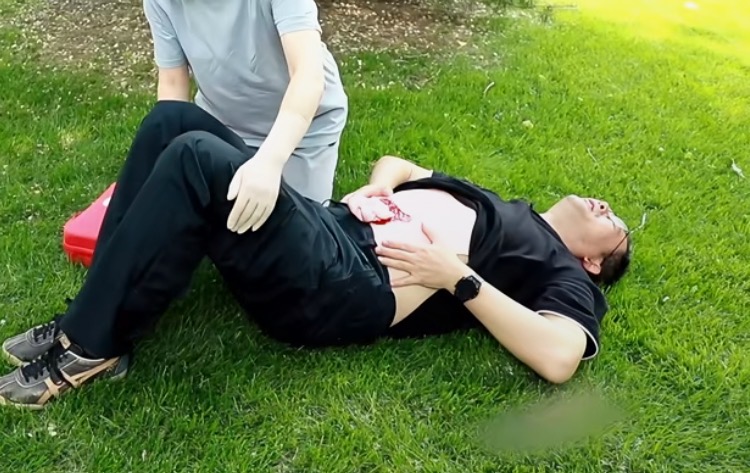
4. Emergency Treatment
Immediate care for abdominal evisceration is crucial. The main goals are to prevent further contamination, minimize tissue damage, and prepare for surgical repair. The following steps outline proper emergency management:
4.1 Initial Assessment
- Assess airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs).
- Control bleeding using sterile pressure dressings.
4.2 Protect the Exposed Organs
- Do not attempt to push organs back inside.
- Cover with sterile, saline-moistened gauze or a sterile plastic wrap.
4.3 Prevent Hypothermia and Shock
- Keep the patient warm and calm.
- Start IV fluids to maintain circulation.
4.4 Transport to Surgical Facility
- Transfer immediately to an operating room for surgical closure and repair.
5. Surgical Management
The definitive treatment for abdominal evisceration is surgical. During the operation, surgeons perform the following:
- Thorough irrigation and cleaning of the wound to remove contaminants.
- Assessment of bowel viability — necrotic tissue is resected.
- Layered closure of the abdominal wall using strong sutures or mesh reinforcement if necessary.
- Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent infection.
6. Prevention and Safety Measures
Preventing abdominal evisceration primarily involves safe surgical techniques and proper postoperative care. Key strategies include:
- Ensuring tension-free sutures and robust wound closure.
- Monitoring patients at risk for wound dehiscence.
- Encouraging controlled coughing and wound support post-surgery.
- Proper wound hygiene and infection control measures.
7. Importance of Medical Simulation Training
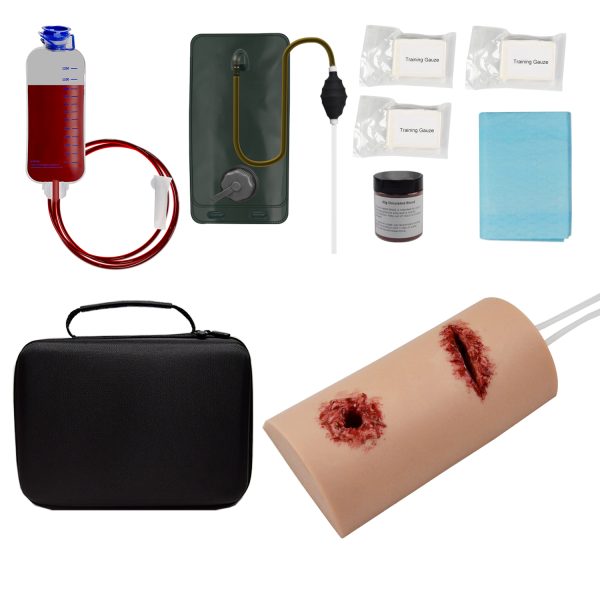
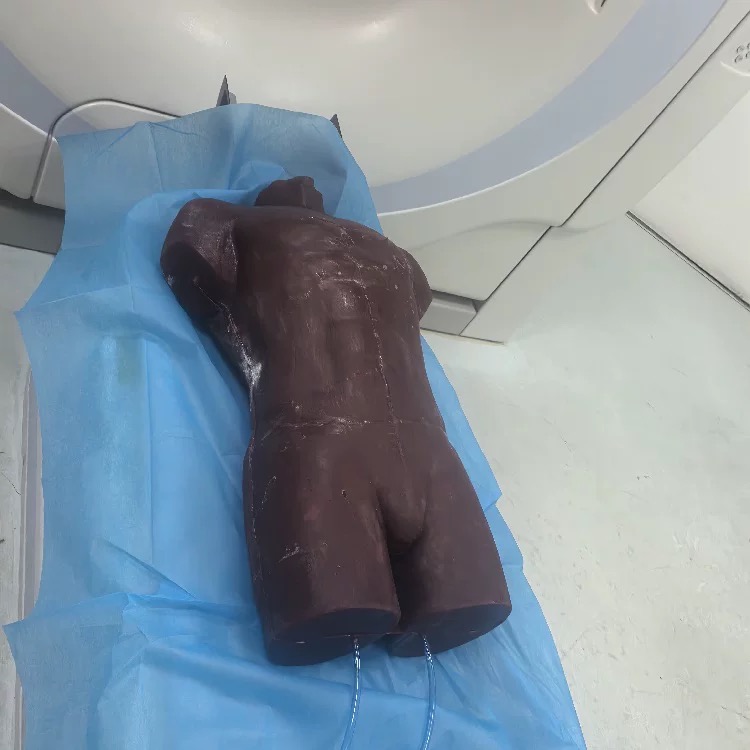
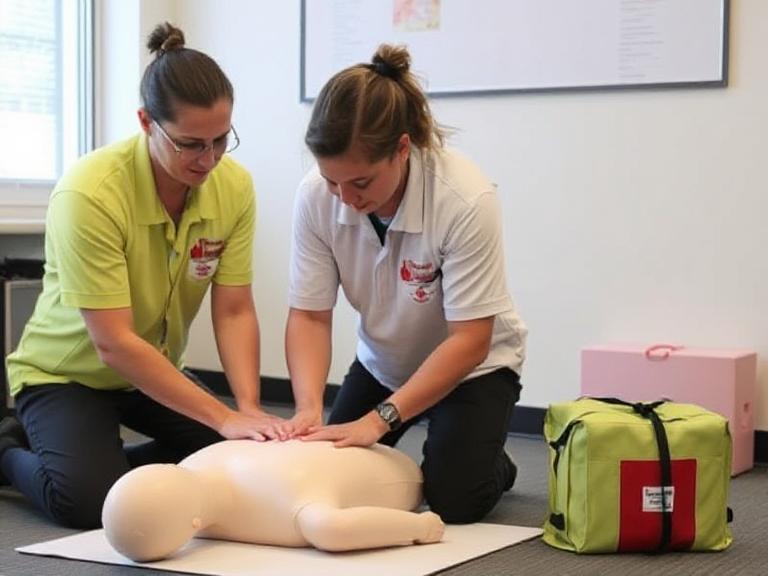
Medical professionals must be adequately trained to handle emergencies like abdominal evisceration. Simulation-based education allows practitioners to practice interventions safely and effectively.
Using realistic medical models helps clinicians gain confidence and proficiency in wound management, suturing, and trauma care before dealing with real patients.
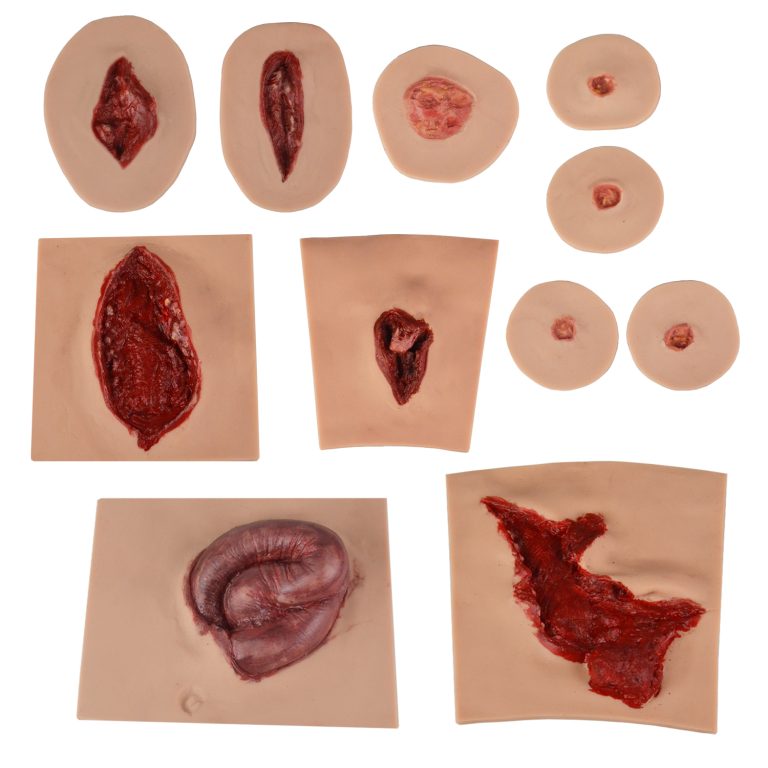
8. Company Spotlight: Medtacedu

Medtacedu specializes in high-quality silicone and plastic models for tactical training, medical education, and science instruction. The company provides a diverse range of innovative educational models—from standardized products to fully customized solutions—trusted by healthcare institutions globally.
8.1 What Our Products Can Do
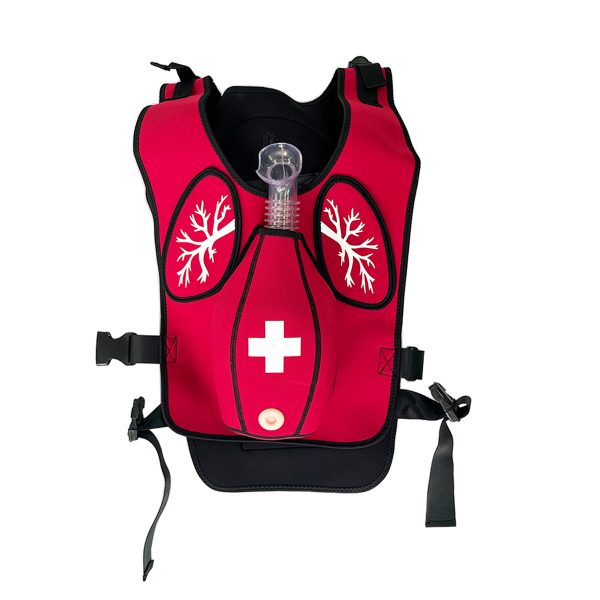
- Tactical Training: Wound dressing models, trauma manikins, and complete emergency response kits.
- Medical Demonstration: Silicone models for disease representation, surgical practice, and device testing.
- Science Education: Veterinary and anatomical education tools for schools and research facilities.
- Injection Models: Training models for ID/SC/IM/IV injection and facial aesthetic procedures.
8.2 Why Choose Medtacedu?
- Extensive product range covering medical, tactical, and educational needs.
- Over 16 years of model production experience, with more than 6 years specializing in medical models.
- Custom design support to bring client ideas to life.
- Commitment to quality, precision, and realism in every model.
8.3 Our Products
9. Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Protrusion of abdominal organs through a wound |
| Main Causes | Trauma, postoperative complications, spontaneous dehiscence |
| Symptoms | Visible organs, pain, bleeding, shock |
| Emergency Care | Protect organs, prevent infection, surgical repair |
| Prevention | Proper wound closure, infection control, patient care |
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is abdominal evisceration life-threatening?
Yes. Without prompt surgical intervention, abdominal evisceration can lead to infection, sepsis, and death.
Q2: What should you do first if you witness an abdominal evisceration?
Call emergency services immediately, cover the wound with moist sterile gauze, and do not push organs back inside.
Q3: Can abdominal evisceration occur after surgery?
Yes. It can result from wound dehiscence due to infection, poor suture strength, or excessive strain on the incision.
Q4: How do medical professionals train for such emergencies?
They use realistic medical training simulators to practice evisceration management in controlled environments.
11. References
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Surgical Safety Guidelines
- American College of Surgeons – Trauma Care and Emergency Surgery Manual
- PubMed Central – Clinical Case Reports on Abdominal Evisceration
- Medtacedu – Official Medical Simulation Product Catalog