In the intricate anatomy of the human throat, a small, V-shaped depression plays an outsized role in keeping us safe every time we swallow and is a critical guide for life-saving medical procedures. This structure is called the vallecula.
Understanding the vallecula is essential for healthcare professionals, particularly those involved in airway management like anesthesiologists, intensivists, and emergency room doctors.
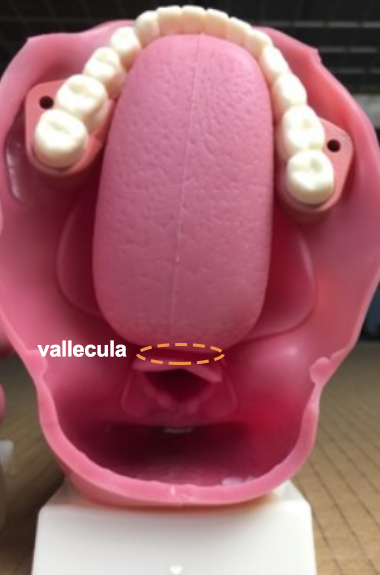
What Is the Epiglottic Vallecula?
The epiglottic vallecula is a small, V-shaped groove or pocket located at the base of the tongue, just in front of the epiglottis. It is formed by the space between the median and lateral glosso epiglottic folds.
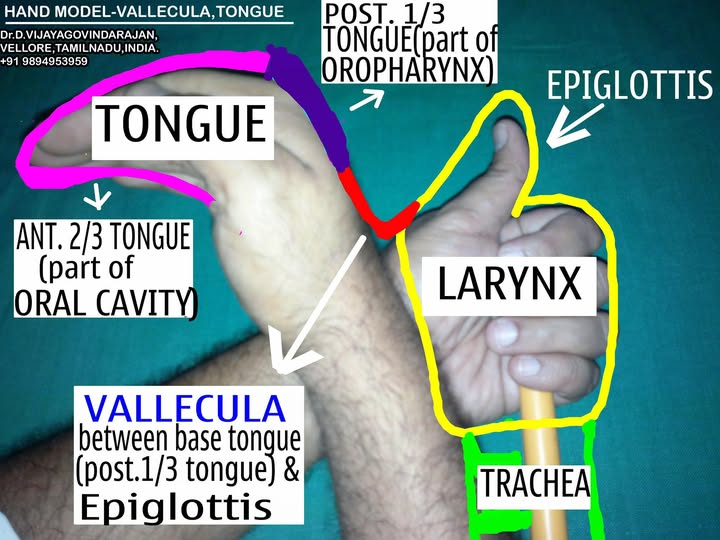
A simple hand model, as described by Dr. Vijayagovindarajan of ENT Easy, can help visualize it:
•VALLECULA is the region between the base of the tongue (posterior third) and the lingual surface of the epiglottis.
•It is a part of the oropharynx.
•It is divided into right and left valleculae by the median Glosso-Epiglttic fold.
Its Primary Function: The Swallow Reflex
During swallowing, the vallecula acts as a temporary “spillway” or channel for food and liquids. This function helps direct material around and away from the elevated epiglottis, ensuring it passes safely into the esophagus and not the airway (trachea). This is a fundamental mechanism for preventing aspiration pneumonia.
The Vallecula’s Crucial Role in Endotracheal Intubation
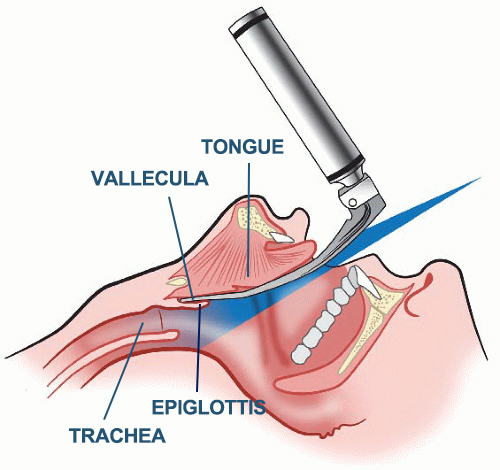
Beyond swallowing, the vallecula is perhaps most famous as the key landmark for the most common method of endotracheal intubation—a procedure to secure a patient’s airway with a breathing tube.
This process primarily uses the Macintosh laryngoscope blade, which is specifically designed to engage the vallecula.
How the Vallecula Aids in Intubation:
1.Perfect Blade Placement:The tip of the Macintosh laryngoscope is advanced over the tongue until it rests securely within the vallecula.
2.Indirect Epiglottis Lift: Applying upward force at this point lifts the hyoid bone and the attached epiglottis indirectly, revealing a clear view of the vocal cords and the glottis opening.
3.Optimized Alignment:This technique provides better alignment of the oral, pharyngeal, and laryngeal axes, making the passage of the endotracheal tube into the trachea significantly smoother and more successful.
4.Reduced Trauma: By avoiding direct pressure on the delicate epiglottis, the method minimizes tissue trauma and potential complications.
Common Challenges & Pro Tips for Intubation:
•Inadequate Lift:If the blade is placed too shallowly, it will fail to lift the epiglottis sufficiently, obscuring the view of the vocal cords. The solution is to gently advance the blade deeper into the vallecula.
•Excessive Pressure: Using excessive force can cause injury to the base of the tongue, the vallecula itself, or the teeth. The key is controlled, upward lifting force, not a levering motion.
•Anatomical Variations: Patients with a deep vallecula or a long epiglottis (“omega-shaped” epiglottis) may require slight adjustments in blade angle or a different blade type.
Common Pathologies of the Vallecula
While a crucial landmark, the vallecula is also a site where medical issues can occur:
•Retention Cysts: These are benign, fluid-filled cysts that can form due to blocked mucous glands. They are often discovered incidentally.
•Foreign Bodies:The vallecula is a common trap for small, sharp foreign objects like fish bones or pins.
•Carcinoma: The vallecula is a subsite of the oropharynx and can be a primary location for squamous cell carcinoma, often associated with HPV.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Groove
The vallecula is a vital functional structure for safe swallowing and the undisputed key landmark for successful direct laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation.
Mastery of its anatomy and function is fundamental for any medical professional involved in airway management, ultimately improving patient safety and procedural success rates.
